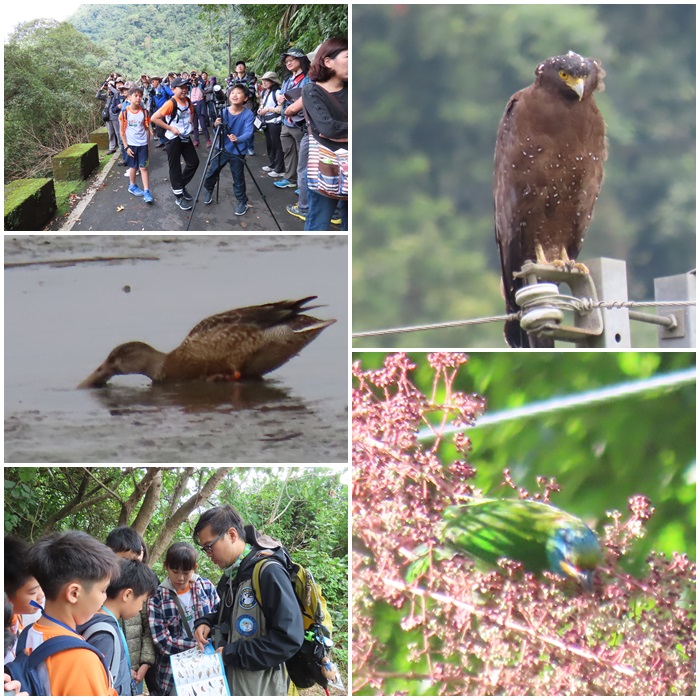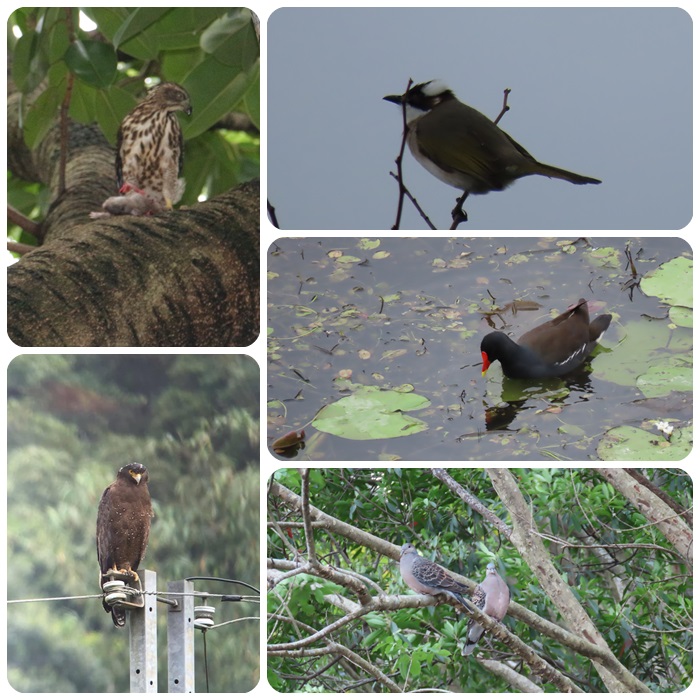




| Basic understanding of birds | ||
Birds are the general name of Aves animals, and
they are the only dinosaurs that have survived to this day. They have
two feet and are thermostatic. Most birds have a body temperature that
is higher than human body temperature. They are oviparous, and their
forelimbs are specialized into wings. Most birds can fly, and there are
a few birds that cannot fly and can only walk. There are no teeth in
the mouth of the bird, and the mouth is called a “beak”. The bird has
various colors of feathers and a streamlined body, allowing them to
fly, land, or dive. A bird is a vertebrate that breathes by air sacs. Aves is a name that is used to classify organisms from scientific taxonomy. Scientific taxonomy is also called biotaxonomy, which is divided into systems, domains, circles, gates, classes, orders, families, genera and species based on levels. As far as birds are concerned, the birds belong to the animal kingdom- Chordata -Aves. There are 21 orders, 94 families, 304 genera and 790 species under the Aves. | ||
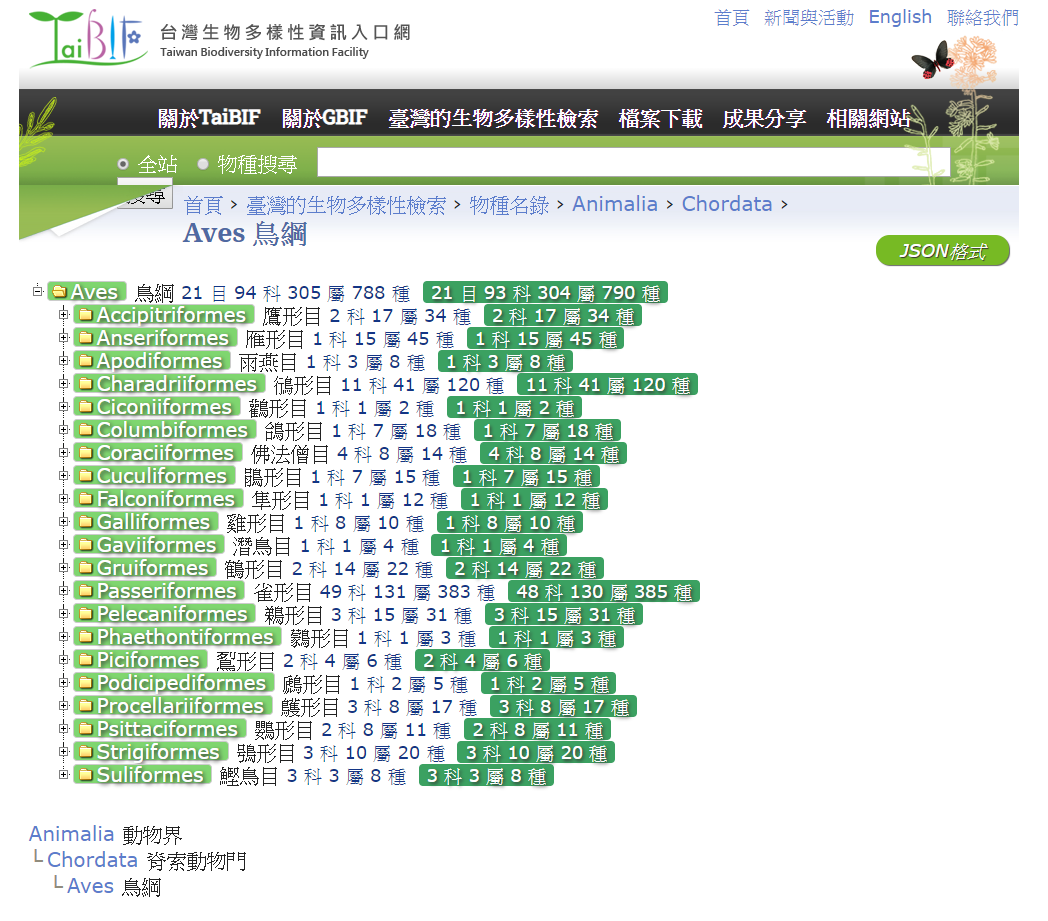 | ||
As there are many species, we can refer to the Taiwan
Biodiversity Information Portal to inquire about bird species.
Understanding bird species is very helpful for us to understand birds,
and it can also help us quickly understand bird classification. | ||
| ||
| Filmed by Bird Conservator | ||
| Bird naming
How do we name birds? In fact, the same creature
will have different names in different places. These names are called
common names, for example: sparrow is the common name. It is not easy
to communicate if each region or country has different names for the
same creature. In order to avoid these confusions, the Swedish
biologist Linnaeus invented the “binomial nomenclature” in 1758, so
that each creature has only one name, called scientific name, which is
convenient for international use. The scientific name is composed of the genus name and the species name. The genus name precedes the species name, and it is written in Latin italics, but the first letter of the genus name is uppercase. The species name is lowercase. For example of, the scientific name of Mikado pheasant is Syrmaticus Mikado. As suggested by Muji Hsiao's book of 100 common Wild Birds in Taiwan, we can first grasp the names of various parts of them, such as head lines, head parts, whole body parts, and flying parts. The second is to master the size and proportion, it is about 15cm for sparrows, it is about 30cm for turtledoves, and it is 53cm for toucans. The third is the external shape observation, like mouth shape, claw shape, wing shape, tail shape, body shape, take mouth shape for example, the raptor's beak-shaped hook can be carnivorous, the warbler’s mouth is short and suitable for eating insects and fruits, and the duckbill is flat so as to filter or can be herbivorous. The fourth is behavior observation, including flight mode, habitat mode, walking mode. We have also found that it was not easy to track birds with the naked eye. It is hoped that telescopes can help to increase the field of vision, but if the birds are hiding in the woods, we must listen to the sounds of bird calls to assist in positioning. | ||
























