|
 Power Generation ¢@ Hydroelectric Plant
Power Generation ¢@ Hydroelectric Plant

 History
History
In 1905, the construction of
the Guishan Power Plant in Xindian District of New Taipei
City was completed and it was the first hydropower plant in
Taiwan. There are four main hydro power plants which are
Guishan power plant in Xindian, Guishan power plant in Wulai,
Houli power plant in Taichung, and the Zhumen power plant in
Kaohsiung. In particular to two power plants in Xindian and
Wulai, they leaded to the prosperous commercial development
of Taipei. Another Houli power plant in Taichung brought the
economic benefit around the middle district of Taiwan
because the power transmission to Daijiaxi area so that
people lived there could work at night. Moreover, Zhumen
power plant in Kaohsiung offered power to agriculture there.
After Taiwan¡¦s economic situation stabilized, the Japanese
began planning to develop the hydropower resources of
Zhuoshui River and opened up the hydropower project in Sun
Moon Lake.
|
 |
 |
|
The power plant near
the Feitsui Reservoir |
Guishan Power Plant in Sindian, New Taipei City |
Hydropower is a renewable energy source
and the most important natural energy source in Taiwan.
After the end of the Second World War, hydropower was the
most important mode of power generation at that time,
accounting for 93.3% of the total power generation, and the
rest was coal-fired power generation, accounting for 6.7%.
At present, Taipower has ten hydropower plants with an
annual generating capacity of 4.5 billion kWh, though the
hydropower generation accounted for only 1.4% of power
generation in 2017. In order to increase green power,
hydropower, which is a renewable energy source, has received
renewed attention in the future.
|
 |
 |
|
The old hydroturbine of Long-Jian Power Plant in Hualian
County (exhibition in Guishan Power Plant) |
The old hydroturbine components of Ching-Shan Power Plant
near Dajia River (exhibition in Guishan Power Plant) |
 Theory
Theory
The principle of hydropower
generation is to use the conversion of potential energy and
kinetic energy, for example, from the high water source of a
river or reservoir to the lower position, the water flow
pushes the turbine to rotate, and drives the generator to
work.
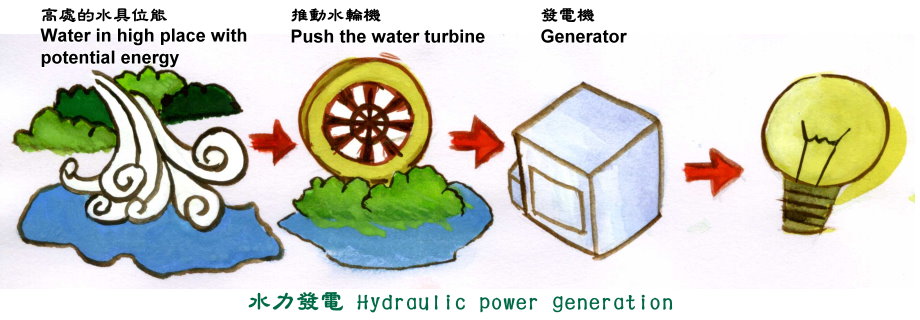
Hand drawing
Hydropower generation can be divided into
conventional power generation and pumping power generation
according to the operation mode, while conventional power
generation is divided into Run-of-the-river
hydroelectricity, retention basin, and ervoir type. The
conventional hydropower plants will build a river dam at a
high point, and the water after passing the generator is
still very clean, so it can also become industrial water and
downstream tap water. In addition to water storage and power
generation, the design of the reservoir dam can also prevent
floods. However, compared with pumped storage power and
conventional hydropower, it has a design of upper and lower
pool that conventional hydropower doesn¡¦t.
¡@
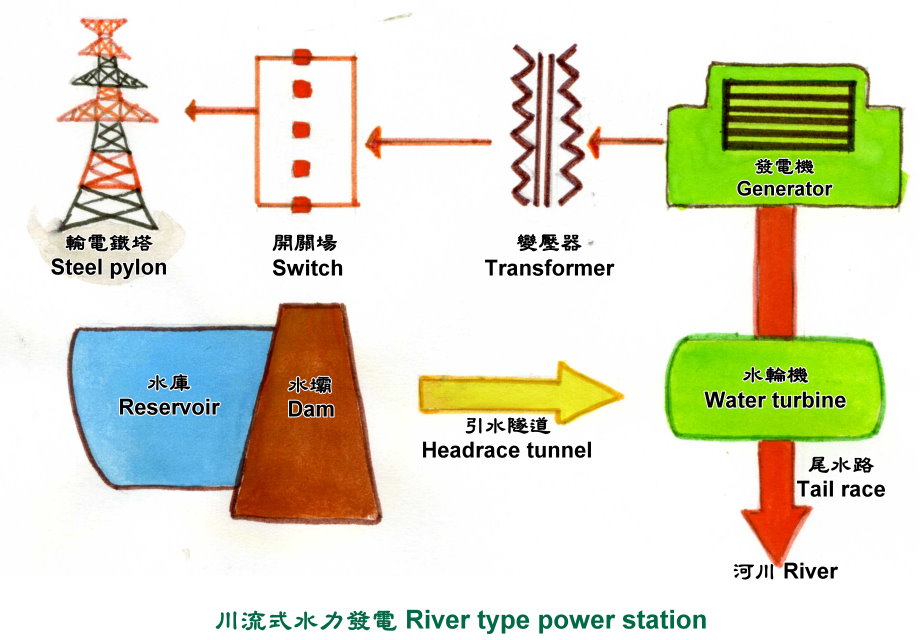
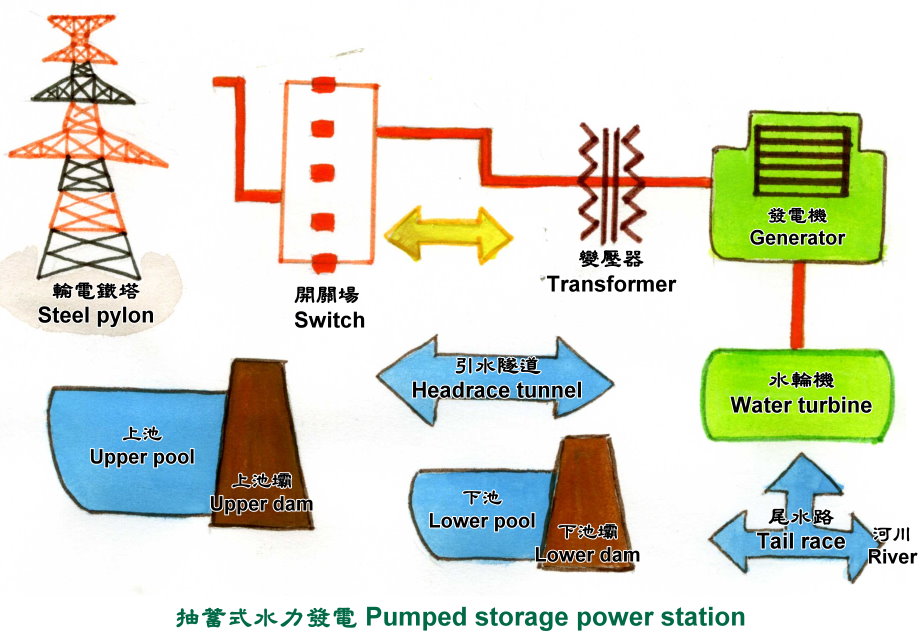
Hand drawing
 Current Situation
Current Situation
¡·Pros :
1.Environmentally friendly renewable energy can be reused.
2.Low operating costs. The process does not emit carbon
dioxide and other air pollutants.
3.Fast start. It is suitable as a peak load power supply.
¡·Cons:
1.The construction cost is high and the construction period
is long (about 10 years).
2.It is difficult to find a suitable location for the
construction of the dam now.
3.Due to limited water resource utilization, it is unable to
generate electricity for a long time.
|
 |
 |
|
Ming-De Reservoir |
Building dams will change habitats |
Taiwan is trying hard to develop green
energy currently. Although it is impossible to build a large
hydropower plant, we have found that we can use large
channels or streams to develop ¡§small hydro¡¨ and generate
electricity from turbines. It is still potential to provide
electricity for small communities or farms.
 |