Effects on Environment Protection
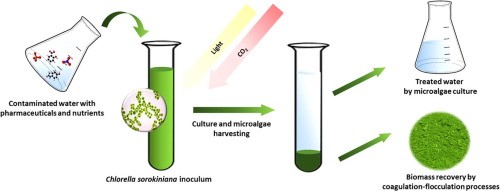
Diagram of Wastewater Processing
Wastewater contains many organic and inorganic pollutants that cause severe damage to the environment and humans' health. Therefore, contaminants should be eliminated before being flown into sensitive areas. Different methods of wastewater purification can be applied for pollutants removal. However, some technical and economic limitations exist on each of them. Thus, new methods of nutrients removal by microalgae based on their phytoremediation ability become future methods due to their viability. Phytoremediation is the use of algae to remove or reduce inorganic nutrients and xenobiotics in the wastewater. It is a reliable process for biotransformation and detoxification of a variety of pollutants. The research focused on the potential of a strain of the green microalgae, Chlorella, to reduce various pollutants in tannery wastewater. The microalga was grown in tannery wastewater for 21 days, and the resultant removal, reduction, and biotransformation of several pollutants such as chromium and chemical oxygen demand, etc., was monitored. Most notably, complete removal of chromium was observed by the 12th day of the culture period. Levels of chemical oxygen demand in tannery wastewater were reduced by 94.74 % after 21 days. The isolation ability of Chlorella Vulgaris is promising for bioremediating and detoxifying tannery wastewater to improve its quality to be qualified for effluent restriction.